Among the diseases of the musculoskeletal system, osteoarthrosis is a frequency leader.It is believed that the vast majority of the population of the planet by the age of 60 has the initial signs of changes in the articular cartilage, and 14% already have manifestations of osteoarthrosis.The most common version of this disease is osteoarthrosis of the knee joints.
Still, "arthrosis" or "arthritis"?
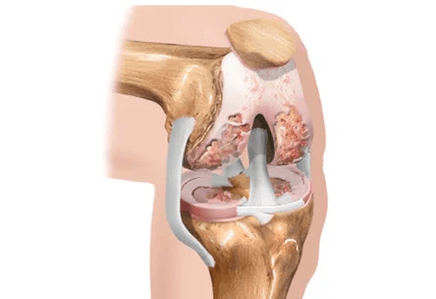
Do not mix these two concepts.Arthrosis is the process of changing primarily the structure of the joints, and arthritis is an inflammation that could occur both against the background of the “untouched” structure and against the background of arthrosis.
Changes in bone with arthrosis can be compared, for example, with knotted growths on a tree trunk, which grows close to the concrete fence and puts pressure on this fence with all its weight.
Normally, the surface of the bones facing each other are separated by two layers of cartilage and meniscuses (additional cartilaginous plates).In addition to the role of the “buffer” between the bones, the cartilage provides the glide of the bones and the mechanical correspondence to each other.Meniscus, which, due to large or small (but frequent) injuries, and also lose their elasticity, can completely or partially break up even more.
With age, and especially in the presence of a hereditary predisposition, articular cartilage is thinner.That is why the bones of the hips and lower legs, which make up the knee joint with their ends, are dangerously approaching each other, friction may even arise between them.
Usually in parallel with the thinning of the cartilage over the years, another unpleasant event occurs: the amount of intra -articular fluid decreases.This liquid is not only a purely mechanical “lubrication” of the joint from the inside.It provides nutrition of bones, menisci and joint cartilage.Violation of the "supply" of all these structures is a real disaster for the joint!
If there is a physical overload of the joint, then bone outgrowths appear on the surfaces of the bones and begin to grow, more similar to pointing, or spikes.For the knee joint, such overloads will be the lifting of weights (including the overweight of your own body!), Physical work with an emphasis on knees (for example, weeding the garden), constant walking on the stairs, running, wearing uncomfortable shoes, flat feet and many others.Now it is easy to imagine what is happening inside the knee joint during the development of arthrosis, and how it manifests itself in appearance.
How does the joint work?
Each of us has seen the joint cartilage many times at the end, for example, chicken bone.It covers small areas of contacting bones.Under the articular cartilage is a subchondral or pericipated bone.The human musculoskeletal system is arranged in a similar way.
Most of the joints of the person consist of bones, synovial (articular) shell and intra -articular fluid.
What happens to the joint with arthrosis?
Under the influence of all those loads that have already been mentioned, there is a compaction and growth of the slim bone, as a result of this, increased trauma of the articular cartilage.
Products of the cartridge of the cartilage formed due to microtrauma fall into the synovial fluid.It is so arranged by nature that they are foreign substances for the synovial shell and provoke its inflammation.The formation of synovial fluid is disturbed, which is usually a sort of “conveyor”, similar to a continuous cycle of enrichment and purification of blood.In addition, the joint fluid becomes less than hyaluronic acid.It is worth telling about this acid.
Hyaluronic acid provides the viscosity of the synovial fluid, creates the “buffer effect” and the “lubrication effect” between the bones, reducing their friction against each other.It is thanks to this substance that the articular fluid in consistency resembles egg protein, not water.Another important role of hyaluronic acid is to ensure the delivery of nutrients from the articular fluid deep into the articular cartilage, since there is nowhere to take the nutrition to it: blood vessels are not suitable directly to the cartilage.In the same way, the “spent” substances from cartilage into the joint fluid are removed: using hyaluronic acid molecules.
So, an enhanced bone seal occurs and unbearable conditions are created for articular cartilage.
The cartilage receives a signal to adapt to these extreme conditions, and its change begins, in another way it is called remodeling.This is mainly manifested by a decrease in the elasticity of cartilage.
In the late stage of the development of arthrosis, the bone becomes rigid, but at the same time more fragile, the cartilage itself is partially impregnated with calcium - calcified.
Symptoms
The development of arthrosis begins with slight pain in the knee, appearing after walking the stairs, physical activity, long walking on foot.Such mild pain can appear for several months, or even years.Then they become more pronounced.At the initial stage of development of the disease, the knee bones are not deformed, but a slight swelling of the joint itself can be observed.
In the second stage of the development of the disease, the pain becomes more intense and occurs after a slight load.In addition to pain, a crunch appears in the knee joint, which differs from the usual soft abuse of a healthy joint with pain.In addition, the deformation of the joint becomes noticeable, the bones to the touch become wider and rude.Bearing the knee more than 90 degrees becomes problematic.
In the third stage of the disease, the knee pain becomes severe and constant, not even passing even in the rest period.The mobility of the knee becomes minimal, often it does not bend more than 90 degrees and does not extend to the end.The deformation of the bones of the joint becomes so strong that there is a valgus (x-shaped) or varability (o-shaped) curvature of the legs.
Diagnostics
Inspection

In the early stages of the disease, the joint is not changed, mobile, the muscles around it are preserved, and strong enough.Only by palpation (pressure) of certain points, more often on the inner surface of the joint, is local (local) pain determined.The doctor asks the patient to perform several squats, bend, straighten his leg in the knee, puts his face up on the couch and leads flexion-extensions himself (this is called “passive” movements).In this case, in addition to pain and limiting the volume of movements, you can determine the crunch, clicking of the joints.With a pronounced inflammatory component, the joint is increased in size, it seems that it is “pumped up” with liquid.With a far -reaching process, bending in the knee can be partially or completely absent, when examined, the surface of the joint seems uneven, tuberous, the limb can be curved (displacement of the axis of the limb, “conjured”).
Laboratory and instrumental research
- The mandatory laboratory survey program includesGeneral, biochemical and immunological blood tests, urine analysis.In the general blood test, attention will be paid: the increased level of leukocytes and the increased rate of erythrocyte settlement, which indicates inflammation.In the biochemical analysis of blood, the metabolic metabolic indicators are important, the level of “liver” enzymes.In immunological analysis, the presence or absence of signs of systemic inflammation will be determined-this is evidenced by the level of C-reactive protein.Urine analysis will reveal the content of "sand" - uric acid crystals.
- Analysis of synovial (articular) fluidIt is prescribed in the case when this liquid is in sufficient quantities.That is, when the joint is swollen, swollen.In conditions of compliance with sterility, the doctor pierces the joint capsule in a strictly defined place, inserts the needle into the joint cavity, and then removes excess fluid.Part of the material obtained enters the laboratory for analysis.At the end of the procedure, the anti -inflammatory drug from the glucocorticosteroid group is most often administered into the joint cavity (for example, Diprospan).
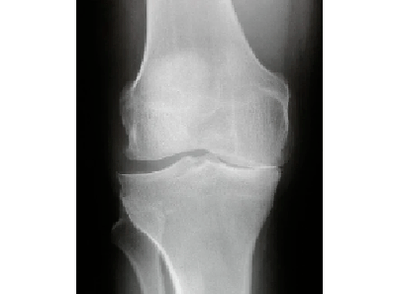 radiography.A picture of both knee joints is mandatory, this is necessary for comparing a sick knee with a healthy one.In the picture, attention is paid to the width of the joint gap (it is judged by the state of meniscus and cartilage), the presence or absence of bone spikes-osteophytes, signs of destruction (destruction) of bones.
radiography.A picture of both knee joints is mandatory, this is necessary for comparing a sick knee with a healthy one.In the picture, attention is paid to the width of the joint gap (it is judged by the state of meniscus and cartilage), the presence or absence of bone spikes-osteophytes, signs of destruction (destruction) of bones.- Ultrasound of the knee jointsHe will answer questions about the preservation of meniscus, the presence of a baker cyst, the severity of inflammation, the presence or absence of uric acid crystals (in the presence of gout).
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).This study is prescribed if an ultrasound does not give an exhaustive answer to questions of a specialist.MRI is mandatory for those patients who are planning to conduct arthroscopy.
- Arthroscopy.Allows you to visualize, that is, personally assess the condition of the joint.The method is indispensable for controversial diagnoses, suspicion of traumatic damage to meniscuses and ligaments (then directly during the study, it is possible to quickly remove torn meniscus or ligaments).
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
The principles of comprehensive treatment should be followed, which include:
- Detailed awareness of the patient about the disease
- The use of physiotherapy exercises, which includes: specific exercises for the joints in the lying position, swimming
- Maintaining optimal body weight
- Wearing an orthosis (soft bandage or at least an elastic bandage) during an increased load on the joint - on the road, during a walk, and so on.
- Non -kerative methods (physiotherapy).This type of treatment gives excellent results precisely with arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis).Apparently, this is due to the fact that the joint is available for the influence of factors such as magnetic and laser radiation.To treat the knee joint, you can use magnetic currents, UHF, cryo-exposure (translated from Greek means the effect of cold).Physiotherapeutic procedures are widespread, treatment courses are usually short -lived - 10, maximum sessions daily or every other day.It should only be remembered about possible contraindications, which include tumor processes, diseases of the thyroid gland and pelvic organs, as well as systemic (autoimmune) inflammatory diseases.
- Drug therapy.

Principles of osteoarthritis therapy:
- Relieve the pain
- delay the further destruction of joint structures
- Restore the lost joint function.
Nonsteroidal anti -inflammatory drugs
For pain relief, drugs from the NSAID Lee NSAID - non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs are used.They are used in and in the form of applications (application to the skin).Applications (local therapy) are a very effective method, especially when it comes to the early stages of the disease.Before using a gel or cream containing NSAIDs, it is necessary to make sure that there are no changes on the skin, whether it is rash, pustules or cracks.The general rule of local treatment is to use the selected cream or gel at least twice a day, and if unpleasant sensations arise - to cancel to the complete disappearance of these manifestations.Intramuscular administration of painkillers is currently not recommended, since the risk of side effects as a result of administration using a syringe does not decrease, but rather the opposite.In the case of pronounced inflammation, the accumulation of a large amount of fluid, intraarticular glucocorticosteroid drugs is allowed, but it should be noted that this procedure should be carried out no more than 1 time every 3 months.
Chondroprotectors
A higher “step” anti -inflammatory effect with osteoarthritis are chondroitin or glucosamine preparations.They, like NSAIDs, fight with inflammation at the level of thin joint structures, but have fewer side effects, and, most importantly, retain their anti -inflammatory effect several months after the cancellation.
Chondroprotectors are a collective name for a group of drugs containing at the same time chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine - “construction bricks” of cartilage.Despite the apparent high cost treatment with chondroprotectors, their convenience for patients and the effectiveness is difficult to overestimate.Firstly, these substances, accepted inside, are perfectly absorbed from the stomach, and the losses of the drug “along the road” to the cartilage are minimal.Secondly, they are able to suppress inflammation in the joint, and, in addition, reliably slow down the process of destruction of the joint cartilage!Most often they are prescribed courses, because they have a rather long “ace” that lasts several months, and sometimes even up to six months.
Hyaluronic acid -based drugs are the so -called hyaluronates.These funds are sold in the form of prepared syringes for intra -articular administration.Hyaluronets are an artificial synovial fluid.The effect of treatment with this method can last up to 12 months.
Surgical treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
As with arthrosis of the hip joints, in the case of serious changes and persistent loss of function, it comes to the operation.With gonarthrosis, two types of interventions are currently performed: arthrodesis (motionless compound) and endoprosthetics.The first operation is rarely performed, according to special indications, when the installation of an endoprosthesis is impossible for any reason.The result of this operation is that the knee becomes motionless.But it does not hurt.Endoprosthetics operation is much more profitable in terms of function.Recall that with large body weight, this operation is not performed - the risk of complications in the postoperative period is too large.From the moment of removal of the damaged sections of the joint and the installation of the prosthesis until the function is completely restored, no more than three weeks pass.
How can ridiculous osteoarthrosis threaten?
Over time, osteoarthrosis does not turn back, but only aggravates, especially while maintaining provoking factors.Consider the main sources of danger to the health and life of a patient with osteoarthritis.
- Chronic pain of various intensity- A very important risk factor, especially in the elderly.Constantly experienced unpleasant sensations can lead to sleep disturbance, a reduced background of mood and even depression.It is difficult to predict which chain of adverse events pull the listed phenomena.
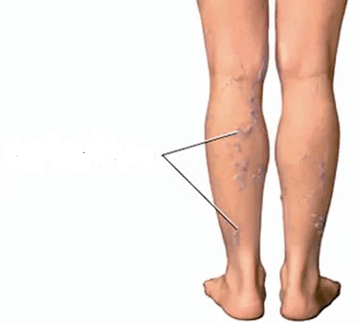
- Pathology of veins.Constant inflammation in the knee area, the growth of bone spikes-osteophytes, which can mechanically injure popliteal vessels, can lead to the development or progression of varicose veins of the veins of the legs.Sometimes orthopedists refuse to operate the knees until varicose nodes are removed, but phlebologists (veins specialists) do not begin surgery in veins until there are pronounced changes in the knee joints.
- Reduced limb function.With a far -reaching process, the joint can completely lose the ability to move, and this, in most cases, is a sign of disability.
- involvement of other joints.We have already found out how such a seemingly ordinary phenomenon, like flat feet, can “pull” the knee joint along and lead to the development of osteoarthrosis.In the same way - along the chain - there is an involvement in the painful process of the knee joint from the opposite side.If the patient neglects the recommendations, refuses to wear a cane, preferring to “limp on his two”, arthrosis of the hip joints develops quite soon.The legs are twisted, the gait becomes a "duck".
- immobility.This serious complication of the disease occurs in cases where the bones of the joint are greatly destroyed, there is no cartilage, the movement in the joint is sharply painful or impossible at all due to the fusion (this is called “ankylosis”) of the bones with each other.In this situation, only surgery can help the patient, but only if it is technically feasible.Overcome is dangerous in the general sense: it causes obesity, osteoporosis, muscle atrophy, the rapid development of diseases of internal organs.In addition, an immobilized person, of course, constantly needs to care for himself.
- Inoperability.Unfortunately, there are a number of states that make the operation impossible, and one of them is far -goed, “neglected” osteoarthritis in patients over 80 with severe related diseases.
Prevention
- Exclude joint injuries.It would seem: there is nothing easier.For a while, abandoning jumps, running, walking on the stairs, dancing, high heels is not at all difficult.In practice, it turns out that it is this point that causes the most protests on the part of patients.A person, if he recently suffers, is usually not ready for the fact that some important point in his daily life will be missed.But if you do not follow these tips, there is a danger of a quick decrease in the quality of life and disability.
- Reducing weight and maintaining it within optimal limits is an extremely important recommendation!No matter how miraculous effect this or that tool has, fat people will not be able to appreciate it.Because while the joints are overloaded with overweight, microtraumas are repeated daily.This can reduce all efforts to “no”.In addition, for some methods of treatment, obesity is a direct contraindication.
- Walking with support.The universal rule for unloading the joint using the support is this: a cane, crutch or handrail should be in the hand opposite to the affected limb.That is, if the right knee hurts, the cane should be kept in the left, and vice versa.
- Correction of flat feet.It would seem, how can flat feet and arthrosis of the knee joint be connected?It turns out directly.If the foot is improperly installed (now we are talking about longitudinal or mixed flat feet, not about the transverse) the load is redistributed in the knee joint.In this case, the severity of the body with a step does not fall on the center of the joint, but on the right or left of it.Accordingly, the right or left meniscus suffers more, and since it suffers more, we wear out faster.Next comes the “queue” of the articular cartilage where the meniscus cannot cope with its function.This process ends with the formation of typical one -sided "arthrose" changes in the knee joint (the appearance of bone outgrowths).





































